A tongue in cheek headline :-). The post is not about body muscle, but about how you can flex your market power (muscle).
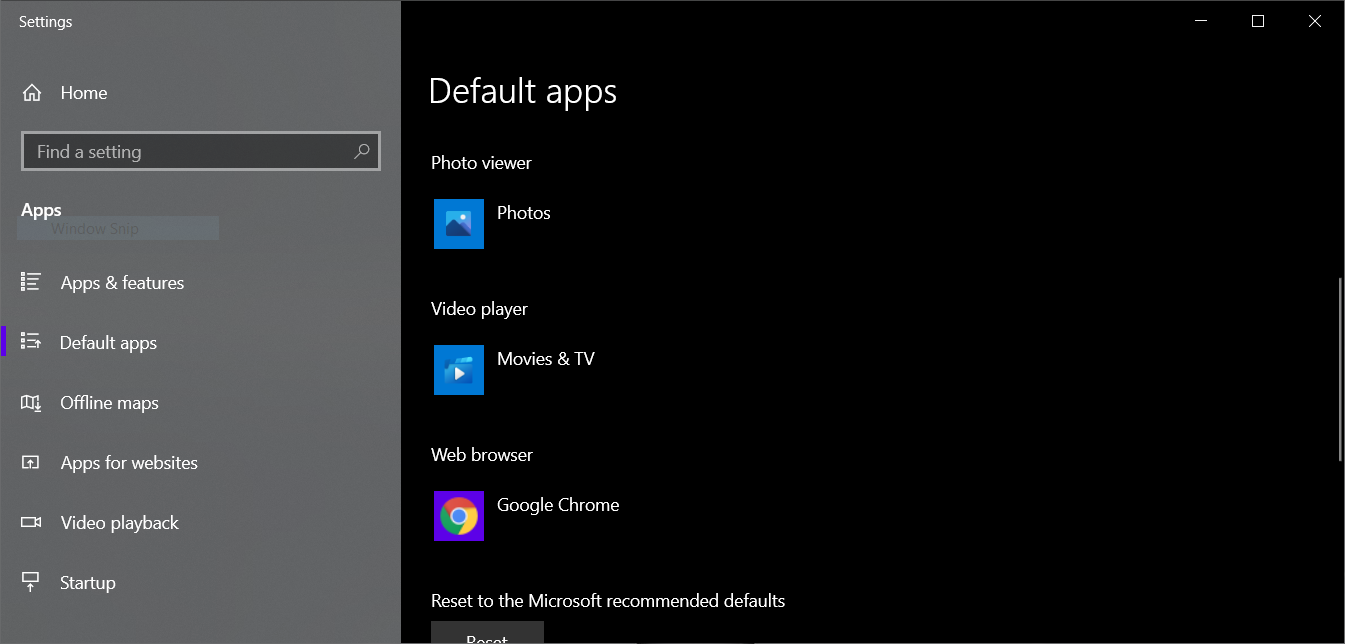
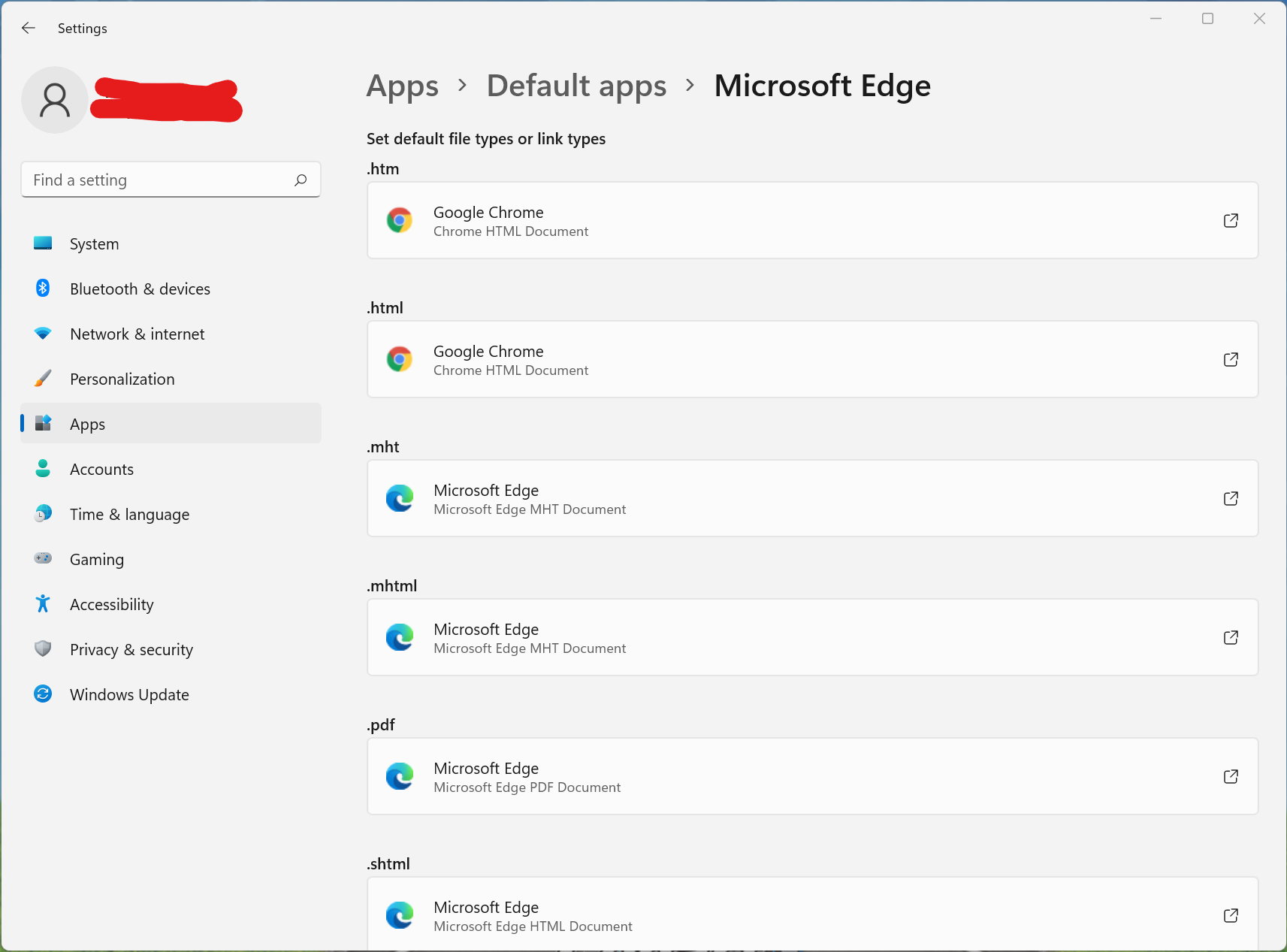
Here is a screenshot comparison of default apps settings in Microsoft Windows 10 and Windows 11. Notice how instead of just giving one option to change the default browser, Microsoft has moved the option to change it by file extension? Does a layperson even know the difference between htm, html, http and https? A clever way for Microsoft to make it a bit more difficult to switch away from edge (Microsoft’s new Internet browser). Some might even call it sinister 🙂
Update Oct 11 : Looks like the main stream media is catching up on this. The Verge has a post on this topic https://www.theverge.com/22714629/windows-11-microsoft-browser-edge-chrome-firefox






